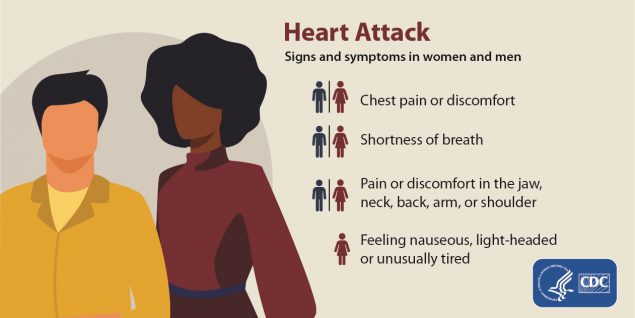
“Women having a heart attack wait longer before
seeking help than men do — one reason women
tend to do worse after a heart attack than men”.1
Umbrella
What may the Heart Attack Umbrella include?
Depending on the Source (DotS) this Umbrella may include:
- Acute Coronary Syndrome
- Acute Myocardial Infarction (AMI)
- Coronary Occlusion
- Coronary Thrombosis
- Heart Attack
- Myocardial Infarction (MI)
Definition
What is a heart attack?
DotS the definition of a heart attack may vary. The (United States) Mayo Clinic’s definition is:
Heart Attack or Cardiac Arrest
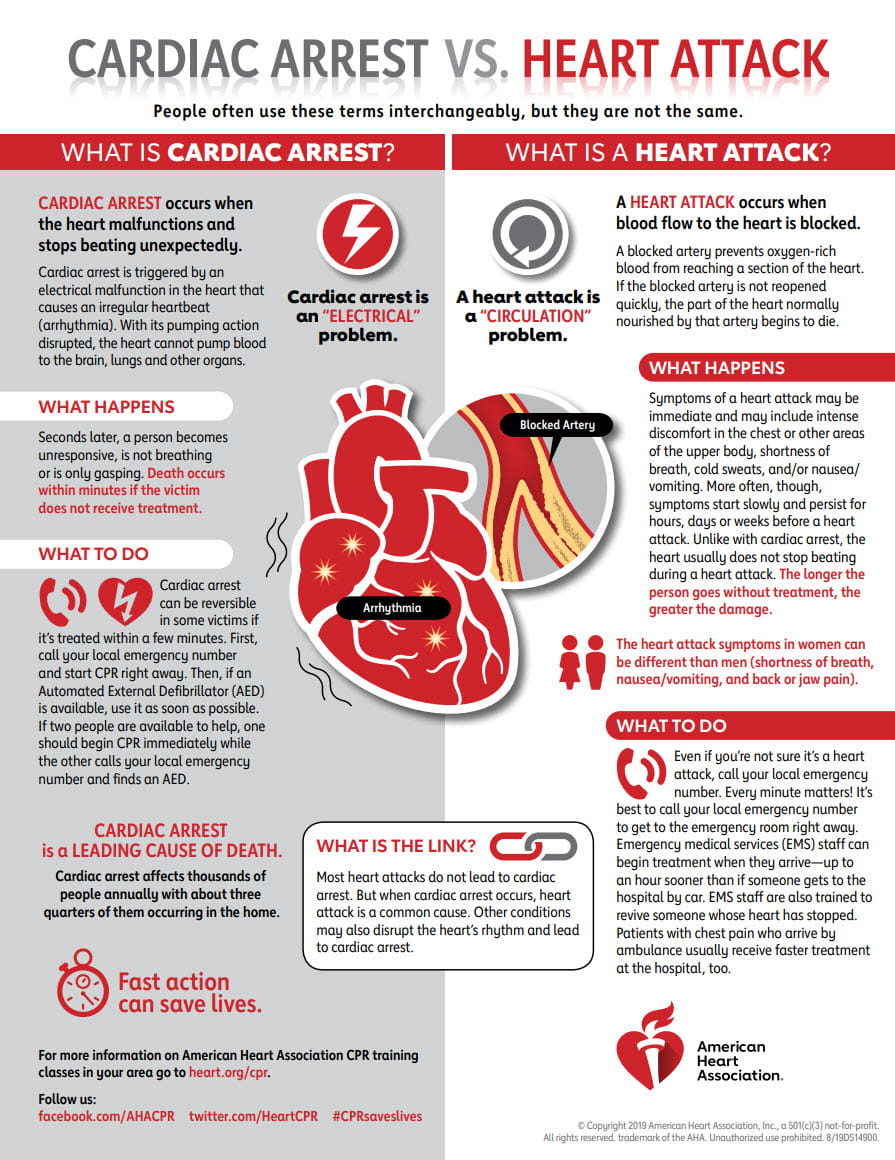
Is a heart attack the same as a cardiac arrest?
In Heart Attack and Sudden Cardiac Arrest Differences the American Heart Association (AHA) explain:
Cause
What causes a heart attack?
In Heart Attack: What Causes A Heart Attack? the British Heart Foundation (BHF) explain:
Women or Not

 In women, how common is a heart attack?
In women, how common is a heart attack?
In Heart Attack Information for Women the [United States] Department of Health and Human Services’ Office on Women’s Health (OWH) elaborate on:
Minutes Matter
Do minutes matter?
Yes. The Heart Attack Information for Women the OWH explain:
The BHF also emphasize:
Minutes Matter Because
Why do minutes matter?
In Heart Attack Information for Women the OWH point out:
Risk Reduction
How can I reduce my risk of having a heart attack?
In Heart Attack: How Can I Reduce My Risk of Having Heart Attack? the BHF explain:
- Keeping active
- Maintaining a healthy weight and diet…
- Limiting how much alcohol you drink…
- Stopping smoking and using other tobacco products
- Controlling high blood pressure, cholesterol levels and blood sugar levels (if you have diabetes)”.9
Health Care Provider
What if I think I am at risk for a heart attack?
If you think you are at risk for a heart attack, it may be in your best interest to choose to talk to your health care provider about this.
Health Topics A-Z
Where may I find Health Topics A-Z related to Heart Attack?
In Health Topics A-Z you may find:
Links
Where may I find Links related to Heart Attack?
Your Country may have Links similar to:

Links
This Links List to third party websites is neither comprehensive nor exhaustive. Inclusion on this Links List does not imply endorsement or recommendation. Non-inclusion on this Links List does not imply non-endorsement or non-recommendation. Third party websites are not under the control of Meno Martha International Menopause Directory. Third party websites may contain explicit medical images and/or sexual references. Please read Meno Martha International Menopause Directory’s Links Policy before proceeding to a Link. Please contact Webmaster if you experience a problem with a Link.New or Updated
- February Is American Heart Month
- Heart Attack Symptoms In Women Are Often Different Than Men [08 February 2024]
- Heart Attack [+ Video: What Is A Heart Attack]
- How To Prevent A Heart Attack
- Mayo Clinic Minute: How A Coronary Calcium Scan Assesses Heart Attack Risk [+ Video Courtesy: Mayo Clinic News Network]
- Warning Signs of A Heart Attack

- About Heart Attacks
- About Heart Disease In Women
- Angina (Chest Pain)
- Angina In Women Can Be Different Than Men
- Aspirin for Reducing Your Risk of Heart Attack and Stroke: Know the Facts
- BMS TV: Coronary Heart Disease (CHD)
- Cardiac Arrest vs. Heart Attack
- Chest Pain
- Common Questions About Heart Attack Symptoms
- Coronary Heart Disease
- Diagnosing A Heart Attack
- FAQs: Heart Health for Women
- February Is American Heart Month
- Get Familiar With Signs of A Heart Attack or Stroke
- Go Red for Women
- Health Topics
- Healthy Lifestyle
- Healthy Living
- Healthy Living
- Heart Attack
- Heart Attack
- Heart Attack
- Heart Attack
- Heart Attack
- Heart Attack
- Heart Attack Information for Women
- Heart Attack Prevention: Should I Avoid Secondhand Smoke?
- Heart Attack Symptoms In Women
- Heart Attack Symptoms In Women Are Often Different Than Men
- Heart Attack Symptoms, Risk, and Recovery
- Heart Attack Symptoms: Know What’s A Medical Emergency
- Heart Attack Timing: Warning Signs [Video]
- Heart Attack Tools and Resources
- Heart Attack Warning Signs
- Heart Attack [+ Video: What Is A Heart Attack]
- Heart Attack and Stroke Symptoms
- Heart Attack and Sudden Cardiac Arrest Differences?
- Heart Attack: Diagnosis & Treatment
- Heart Attack: Prevention
- Heart Attack: Prevention
- Heart Attack: Recovery
- Heart Attack: Screening and Prevention
- Heart Attack: Symptoms
- Heart Attack: Symptoms & Causes
- Heart Attack: Symptoms of A Heart Attack
- Heart Disease
- Heart Disease and Women
- Heart Health Information In Your Language: Heart Attack Warning Signs Action Plans
- Heart Health Information In Your Language: Will You Recognise Your Heart Attack? Fact Sheet
- Heart Health for Women
- Heart-Healthy Eating
- Heart-Healthy Lifestyle Changes
- Heartburn or Heart Attack: When To Worry
- Heartburn or Heart Attack?
- How To Prevent A Heart Attack
- How To Prevent Heart Disease After Menopause
- How To Tell the Difference Between A Heart Attack and Panic Attack
- Ischemic Heart Disease: What Should Women Know?
- Just A Little Heart Attack [Video]
- Keep Your Heart Healthy
- Know Your Numbers They Could Just Save Your Life

- Know Your Risk
- Know the Symptoms
- Lifestyle Changes for Heart Attack Prevention
- Life’s Essential 8
- Make the Call. Don’t Miss A Beat. [Heart Attack Campaign for Women]
- Making Mayo’s Recipes: Two Days’ Worth of Heart-Healthy Menus
- Mayo Clinic Minute: How A Coronary Calcium Scan Assesses Heart Attack Risk
- Mayo Clinic Minute: Signs of Coronary Artery Disease, How To Reduce Your Risk [+ Video Courtesy: Mayo Clinic News Network]
- Mayo Clinic Minute: Women’s Heart Attack Symptoms Vary [+ Video Courtesy: Mayo Clinic News Network]
- Mayo Clinic Q and A: Self-Care Steps Can Keep Your Heart Healthy During the Holidays
- Mayo Clinic Study Indicates Age Has Distinct Influences on Sex-Related Outcomes After Heart Attack
- Nonhormone Treatments for Hot Flashes and Night Sweats
- OfficialGoRed4Women [Videos]
- Real Women
- Recipes [American Heart Association]
- Silent Heart Attack: What Are the Risks?
- Smokefreewomen [United States]
- Stress Management
- Symptoms of A Heart Attack
- Symptoms of Heart Attack & Stroke In Women
- The Heart Truth
- Treatment of A Heart Attack
- Understand Your Risks To Prevent A Heart Attack
- Video Series-2023: Menopause and Heart Disease
- Video Series-2023: NAMS 2023 Nonhormone Therapies Position Statement for Bothersome Menopause Symptoms
- Video Series-2023: New FDA-Approved Nonhormone Option for the Treatment of Hot Flashes
- Warning Signs of A Heart Attack
- Watch, Learn and Live. Heart Attack [Interactive]
- Videos & Podcasts: Videos – Interviews: Cardiovascular Disease In Women
- What Is A Heart Attack?
- What Is A Heart Attack?
- What Is Cardiac Arrest?
- What Is Meant By the Term Heart Age?
- Women and Heart Attacks
- Womenheart.org [WomenHeart: The National Coalition for Women With Heart Disease, United States]
- Women’s Wellness: Understand Heart Disease Symptoms and Risk Factors Unique To Women
- World Heart Day [29 September]

- World Menopause Day

- World Menopause Day [18 October 2023]: Patient Information Leaflet

Sources
Where may I find the Sources quoted?
You may find the Sources quoted at:
Sources
- Heart Attack Information for Women. Page Last Updated: 22 February 2021. Office on Women’s Health, United States Department of Health and Human Services Womenshealth.gov https://www.womenshealth.gov/heartattack/facts.html Accessed: 15 September 2023
- Heart Attack: Symptoms and Causes – Overview. 21 May 2022. Mayo Clinic https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/heart-attack/symptoms-causes/syc-20373106 Accessed: 15 September 2023
- Heart Attack and Sudden Cardiac Arrest Differences. Last Reviewed: 02 December 2022. American Heart Association https://www.heart.org/en/health-topics/heart-attack/about-heart-attacks/heart-attack-or-sudden-cardiac-arrest-how-are-they-different Accessed: 15 September 2023
- Heart Attack: What Causes A Heart Attack? Page Last Updated: March 2023. British Heart Foundation https://www.bhf.org.uk/informationsupport/conditions/heart-attack Accessed: 15 September 2023
- Heart Attack Information for Women. Page Last Updated: 22 February 2021. Office on Women’s Health, United States Department of Health and Human Services Womenshealth.gov https://www.womenshealth.gov/heartattack/facts.html Accessed: 15 September 2023
- Heart Attack Information for Women. Page Last Updated: 22 February 2021. Office on Women’s Health, United States Department of Health and Human Services Womenshealth.gov https://www.womenshealth.gov/heartattack/facts.html Accessed: 15 September 2023
- Heart Attack. Page Last Updated: March 2023. British Heart Foundation https://www.bhf.org.uk/heart-health/conditions/heart-attack.aspx Accessed: 15 September 2023
- Heart Attack Information for Women. Page Last Updated: 22 February 2021. Office on Women’s Health, United States Department of Health and Human Services Womenshealth.gov https://www.womenshealth.gov/heart-attack/facts Accessed: 15 September 2023
- Heart Attack: Can I Reduce My Risk of Having Heart Attack? Page Last Updated: March 2023. British Heart Foundation https://www.bhf.org.uk/heart-health/conditions/heart-attack.aspx Accessed: 15 September 2023



